A Guide to Translation Services for Legal Documents

When you're dealing with international business or legal matters, a single mistranslated clause can completely invalidate a contract. Just one small error can derail an entire court case. This is why choosing the right translation services for legal documents is so much more than just swapping words from one language to another. It’s about protecting your interests, making sure you’re compliant, and preserving the original legal intent across borders. This is a highly specialized field, and it demands absolute precision.
Navigating the High Stakes of Legal Document Translation

Let's be clear: legal translation is a high-stakes game with zero room for ambiguity. It’s not like translating a marketing brochure where a bit of creative flair might even be a good thing. In legal translation, accuracy is everything. The language used in contracts, affidavits, and patents is chosen with painstaking care, and every single word has legal weight.
This need for precision is what’s behind the massive growth in the industry. The global market for legal translation services was valued at USD 5.0 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit USD 7.8 billion by 2031. This boom is directly tied to the increase in cross-border litigation, international M&A, and intellectual property filings. In these scenarios, a simple mistake can easily spark a million-dollar dispute. You can find more market analysis on this trend over at OpenPR.com.
Why Legal Translation Demands Specialized Expertise
Asking a bilingual employee to handle a legal contract is a common but risky move. While their language skills are valuable, they almost certainly lack the specific training needed for legal texts. True legal translation is about more than just fluency. It requires a deep, practical understanding of different legal frameworks—after all, what’s enforceable in one country might be totally void in another.
Expertise is non-negotiable in a few key areas:
- Jurisdictional Nuances: The translator must grasp the legal systems of both the source and target countries. This ensures the terminology isn't just similar, but legally equivalent and enforceable.
- Cultural Context: Legal concepts are often tied to culture. A word-for-word translation can easily miss the intended legal effect, creating dangerous loopholes or misunderstandings.
- Terminology Precision: Words like "indemnity," "liability," and "force majeure" have very specific, rigid meanings in legal language that a generalist translator could easily get wrong.
The real goal of legal translation is to create a document that is not only linguistically perfect but legally solid in the target country. It has to do the exact same job the original document was designed to do.
This guide is for legal professionals and business leaders who can't afford to take chances with their documents. We'll walk through the different kinds of legal translations, break down essential terms like certified and notarized documents, and give you a practical playbook for picking the right service. Understanding what’s at stake helps you avoid costly mistakes and ensures your documents hold up under scrutiny, wherever they end up.
Getting the Right Translation for Your Specific Legal Document
When it comes to legal translation, there’s no such thing as "one size fits all." A birth certificate needed for an immigration visa is a completely different beast than a multi-million-dollar merger agreement. If you treat them the same, you'll either spend a fortune on services you don't need or, worse, submit a document that gets rejected on a technicality.
The first, most critical step is figuring out what kind of document you have. This single decision dictates the level of accuracy, type of certification, and subject matter expertise you'll need from your translation services for legal documents.
Business and Commercial Contracts
Contracts are the lifeblood of global commerce. They spell out rights, responsibilities, and what happens when things go wrong. A single mistranslated term in a distribution agreement, employment contract, or sales agreement can open the door to devastating financial and legal battles.
The goal here isn't just a literal word-for-word swap; it’s about achieving legal equivalence.
- Crucial Terminology: Legal concepts like "indemnity," "jurisdiction," and "force majeure" have very specific meanings. They must be translated to the precise equivalent in the target country's legal system, not just a close dictionary definition.
- Enforceability: The translator absolutely has to understand the legal frameworks in both countries. Their job is to ensure the translated clauses are actually binding and will hold up in court.
For contracts, you need more than a linguist. You need a specialist who understands commercial law and can ensure the original intent of your agreement remains legally airtight across borders.
Litigation and Court Documents
Once you step into a courtroom, the stakes are even higher. Documents like court transcripts, affidavits, witness statements, and judicial orders demand an almost fanatical level of precision. There is zero room for interpretation or creative license.
Think about it: a subtle shift in wording in a witness statement could completely change the perception of intent, potentially derailing an entire case. For these documents, the only thing that matters is verbatim accuracy. The translation must be a perfect mirror of the original, with nothing added and nothing left out. This is where certified translations often become mandatory for the court to even accept the document.
A certified translation for a court filing isn't just a "nice-to-have"—it's a procedural requirement. It's the translator's formal, sworn statement that the text is a complete and accurate copy, which is what gives it legal standing.
Intellectual Property and Patents
Translating intellectual property, especially patents, is one of the most demanding niches in the entire field. A patent is a strange hybrid—it's part legal shield, part highly technical blueprint. Getting it right requires a rare mix of skills.
A patent translator must possess:
- Technical Expertise: A genuine, deep understanding of the specific science or engineering field the invention belongs to.
- Legal Precision: Fluency in the patent laws and specialized terminology of both jurisdictions.
- Linguistic Skill: The ability to articulate complex technical concepts in another language without losing a single drop of nuance.
A mistake in a patent translation can invalidate a claim, weaken legal protections, or cause an outright rejection of the application. This is why top firms often seek out translators who aren't just language experts but also hold advanced degrees in the relevant technical fields.
To handle these high-stakes documents, you'll want to explore specialized legal document translation providers who live and breathe this work. Protecting your IP internationally starts with matching your document to a translator with the right kind of expertise.
Understanding Certified and Notarized Translations
When you’re dealing with legal document translation, you'll constantly run into two terms: certified and notarized. People often use them interchangeably, but they represent two very different levels of authentication. Getting them mixed up isn't just a minor slip-up; it can lead to your documents being flat-out rejected by courts or government agencies, creating massive headaches and delays.
Think of it this way: choosing the right type of authentication is the final, critical step to ensure your translated document is accepted where it matters most. Getting this right from the start saves you a world of stress.
What Is a Certified Translation?
A certified translation is all about one thing: quality and accuracy. It’s not just the translated document itself; it’s accompanied by a signed statement from the translator or translation agency.
This statement, often called a "Certificate of Accuracy," is their professional guarantee. In it, they attest that the translation is a complete and faithful reproduction of the original document. It’s their word on the line.
A proper certified translation package will always include:
- The signed attestation: A formal statement confirming the translation is accurate and complete.
- Translator’s credentials: Information identifying the translator or company responsible.
- A clear link to the source: A reference to the original document to show what was translated.
This is the standard for most official submissions in the U.S., like documents for U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) or evidence you’re submitting in court. For a closer look at the requirements, check out our guide on certified translation services.
When Is a Notarized Translation Required?
Now, a notarized translation shifts the focus from the quality of the work to the identity of the person signing for it. In this process, a Notary Public watches the translator sign the Certificate of Accuracy and then adds their official stamp and signature.
This is a crucial distinction. The notary’s seal doesn't mean they’ve checked the translation or have any linguistic expertise. It only confirms the identity of the signer, adding a layer of security against fraud.
A Notary Public is not a language expert. Their role is purely administrative: to verify that the person signing the certificate is exactly who they say they are.
This extra step is often mandatory for documents intended for use abroad, like international powers of attorney, academic transcripts for foreign universities, or certain high-stakes business contracts where verifying the signer's identity is non-negotiable.
Certified vs Notarized Translation At a Glance
The need for these kinds of official translations is only growing. The legal translation market was already valued at US$ 12.7 billion in 2024 and is expected to climb to US$ 15.1 billion by 2034, largely because of the rise in international litigation and cross-border business. You can see more on this trend over at Fact.MR.
To cut through the confusion, here’s a straightforward table to help you decide which you need based on your situation.
| Feature | Certified Translation | Notarized Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Verifies the accuracy and completeness of the translation. | Verifies the identity of the person signing the certification. |
| Who Performs It | The translator or a qualified representative of the translation agency. | A licensed Notary Public witnesses the translator's signature. |
| Common Use Cases | Immigration documents (USCIS), court evidence, legal contracts. | International powers of attorney, foreign academic records, sworn statements. |
| Key Takeaway | Focuses on the quality of the document. | Focuses on the authenticity of the signature. |
Ultimately, the best way to know for sure is to ask the institution that will be receiving the document. They will always have the final say on their specific requirements.
Choosing Your Method: AI, Human, or a Hybrid Approach?
Figuring out how to translate your legal documents isn't as simple as it used to be. It's not just a matter of hiring a firm anymore. Now, you’ve got a whole spectrum of options, and the choice you make between AI, a human expert, or a mix of both will have a direct impact on the cost, speed, and—most importantly—the reliability of the final document.
Ultimately, your choice has to line up with what the document is for and the level of risk you're comfortable with. A quick AI translation might be fine for an internal review, but using it for a contract you’re submitting to a court? That’s a serious gamble.
The Case for Pure AI Translation
Let's be clear: artificial intelligence has gotten incredibly good at processing language. For specific, lower-stakes legal tasks, AI-powered tools are hard to beat for their sheer speed and low cost.
Think of AI as a powerful first-pass filter. It really shines when you need to get the gist of a massive amount of text—and fast.
- E-Discovery: When you're sifting through a mountain of documents for litigation, AI can be your best friend, quickly flagging potentially relevant files for a human to review more closely.
- Internal Reviews: If your multilingual team is just working on internal drafts of contracts or company policies, an AI translation can give them a solid starting point.
- Cost Efficiency: There's no denying it—AI is significantly cheaper than human translation. This makes it a practical option for preliminary work or high-volume projects on a tight budget.
But here's the catch: AI still fumbles the nuanced language and cultural context that are baked into legal documents. If you're exploring this route, it helps to know what to look for. We've put together a guide on finding good translation software to help you sort through the options.
When Human Expertise Is Non-Negotiable
Despite all the tech advancements, some situations just flat-out require a professional human translator, ideally one who lives and breathes legal terminology. These are the high-stakes scenarios where one tiny mistake can have massive ripple effects.
A human translator is the only way to go when your document requires:
- Certification or Notarization: An AI can't sign a "Certificate of Accuracy." For any document headed to a court or a government agency like USCIS, you need a human-certified translation. Period.
- Deep Cultural Nuance: Translating something like a legal threat or a sensitive negotiation memo isn't just about words. It's about understanding cultural subtleties that machines are blind to.
- Complex Legal Interpretation: Concepts like "liability" or "jurisdiction" don't always have a direct one-to-one translation. You need someone with actual legal knowledge to find the precise equivalent in the target language.
For any document that will be filed with an official body or carries serious legal weight, a qualified human translator is your only safe bet.
Relying on AI for a final, official legal document is like asking a calculator to write a legal brief. It can process the numbers, but it completely lacks the critical judgment and contextual understanding required for the task.
The Hybrid Model: The Best of Both Worlds
This is where things get interesting. The hybrid approach is quickly becoming the go-to for many modern legal workflows. It smartly combines the raw speed of AI with the refined precision of a human expert, giving you a great balance of quality, cost, and turnaround time.
The process is pretty straightforward:
- AI First Draft: An advanced AI tool, like DocuGlot, gets the ball rolling by producing a high-quality initial translation. Crucially, it keeps the original document's formatting intact.
- Human Review and Refinement: A human legal expert or lawyer-linguist takes that draft and polishes it to perfection. They fix any nuanced errors, ensure every legal term is spot-on, and adapt the text for cultural context.
This two-step process lets legal teams power through larger volumes of work much more efficiently without ever compromising on the accuracy required for official use.
This decision tree can help you visualize which path makes the most sense for your specific document.
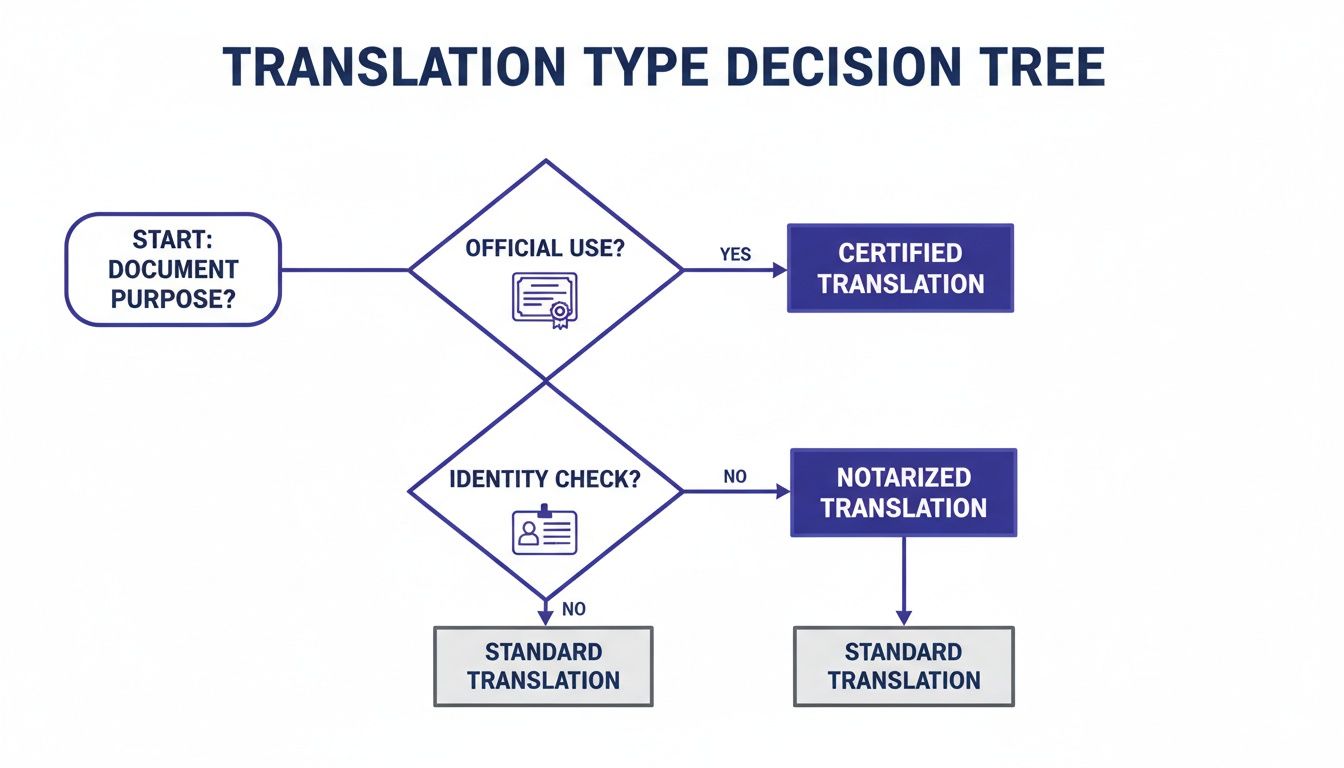
As the flowchart shows, once you enter the realm of official use or identity verification, the need for human-led processes like certification and notarization becomes clear.
The market is definitely responding to this need for sophisticated solutions. The global market for translation services for legal documents is on track to hit USD 27.78 billion by 2025, largely because of the boom in international litigation and IP disputes. This growth underscores just how critical reliable translation is. Platforms like DocuGlot offer a smart entry point, giving you a fast AI translation that preserves your file's integrity before a human expert steps in for the final, certifiable review. By choosing your method strategically, you can keep risks in check without blowing your budget.
Your Pre-Translation Checklist for Flawless Results
Getting a top-notch legal translation isn't just about hiring the right service—it really starts with you. Before you hit "upload" on that file, a little prep work can make a world of difference. It helps you sidestep frustrating delays, keep costs down, and ensures the final document is exactly what you need.
Think of it this way: you wouldn't walk into a courtroom with a disorganized pile of evidence. Handing a messy, half-finished document to a translator is the same kind of gamble. It’s practically asking for errors and expensive, last-minute fixes.
Finalize Your Source Document First
This sounds like a no-brainer, but it's easily the most common and costly mistake I see. Make absolutely sure your source document is 100% final before sending it off. Even one tiny change—a date, a name, a single clause—forces the entire translation to be updated, re-reviewed, and sometimes even re-certified.
Those "quick fixes" create a domino effect, leading to missed deadlines and surprise fees. Nail down the text from the start, and you'll keep the project on track and on budget.
Treat your source document like wet concrete. Once you hand it over for translation, it should be set. Any changes after that point will leave messy, visible marks on the final product and your timeline.
Provide Clean and Editable Files
The format of your document matters more than you might think. A scanned PDF can feel like the easiest option, but it's a major roadblock for any translation service, whether it’s a person or an AI. Scans often have blurry text or weird formatting glitches, and they can't be edited directly.
For the smoothest process, always send over a clean, editable file.
- What works best? Microsoft Word (.docx) or other text-based files are perfect. They let the translator work right inside the document, which is the best way to keep the original layout intact.
- What if a scan is all you have? If a PDF is unavoidable, make sure it’s a high-quality, crystal-clear scan. A poor-quality image forces someone to retype everything or rely on glitchy text recognition software, which is a recipe for inaccuracies and higher costs.
Sending a clean file is the single best thing you can do to preserve the document's formatting—tables, headers, everything—in the final translation.
Create a Glossary of Key Terms
Every legal matter has its own jargon. Your company, contract, or case file is filled with terms, acronyms, and phrases that have a very specific meaning—a meaning an outside translator just won't know.
Putting together a simple glossary is a game-changer for consistency.
- List your core terms: Jot down 10-20 key terms unique to the document. Think project names, internal job titles, or proprietary technology.
- Define or translate them: If you already have approved translations for these terms, great. If not, just add a quick, clear definition in the original language.
- Flag "Do Not Translate" items: Be sure to point out any words, like your company or brand name, that should be left as-is.
This little bit of effort takes the guesswork out of the equation for the translator. It’s a foundational step for anyone who needs reliable translation services for legal documents and wants their unique terminology handled correctly every single time.
Protecting Confidentiality in Legal Translation
When you're dealing with legal documents, you're handling more than just words. You're responsible for client secrets, intellectual property, and sensitive business strategies. Handing those files to a third party means security and confidentiality are absolutely non-negotiable.
A data breach in the legal world isn't just an inconvenience; it can be catastrophic. Think violated attorney-client privilege or exposed trade secrets. This is why you must vet a translation provider's security protocols just as thoroughly as you would their linguistic skills.
The Role of Non-Disclosure Agreements
Your first move should always be to secure a rock-solid Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA). Any professional translation service worth its salt will expect this and should be ready to sign one before you send anything over. If they push back or seem hesitant, that’s a major red flag.
A good NDA for translation work should be specific. Make sure it clearly covers:
- What's considered confidential: This should include the documents themselves, plus any emails or notes related to the project.
- The provider's obligations: Spell out how your data will be handled, stored, and eventually, destroyed.
- How the information can be used: State explicitly that the files are for the translation project and absolutely nothing else.
Don't ever just assume confidentiality is a given. Get it in writing. An NDA ensures everyone who touches your files, from the project manager to the individual translator, is legally bound to silence.
Essential Technical Security Measures
Legal protection is one piece of the puzzle; technical security is the other. The provider’s digital infrastructure is what keeps your data safe from prying eyes. You need to be confident they have robust security practices in place.
Here are the technical safeguards you should look for:
- End-to-End Encryption: Your files must be encrypted from the moment they leave your computer until you get the translation back. This makes the data useless to anyone who might intercept it.
- Secure Server Infrastructure: Don't be shy about asking where your data lives. Reputable services use access-controlled servers that comply with recognized standards like ISO 27001. Understanding the intersection of ISO 27001 and Australian data privacy laws is crucial for ensuring compliance across the board.
- Transparent Data Retention Policies: Your data shouldn't sit on a provider's server indefinitely. A trustworthy partner will have a clear policy on how long they keep your files and will guarantee their permanent deletion after a specific time, often as short as 24 hours.
A provider’s security policy is a direct reflection of their professionalism. If their confidentiality measures are vague or difficult to find, it’s a clear sign to look elsewhere. Your clients' data and your firm's reputation depend on it.
Common Questions About Legal Translation Services
When you're dealing with legal translations, a lot of practical questions pop up. Getting straight answers is crucial—it helps you avoid paying for things you don't need or, worse, submitting a document that gets rejected for not meeting legal standards. Let's tackle some of the most common queries I hear.
How Much Do Legal Translation Services Cost?
There's really no one-size-fits-all price tag for legal translation. Most professional agencies will quote you on a per-word or per-page basis, but that rate is heavily influenced by a few key factors. For instance, translating a dense patent application from Japanese to English is a completely different ballgame than translating a standard contract clause into Spanish.
Here’s what typically drives the cost up or down:
- Language Pair: Common language combinations, like English to Spanish, are almost always more affordable than less common pairings.
- Urgency: Need it yesterday? Expect to pay a premium. Rush jobs that require translators to work after hours or on weekends will naturally cost more.
- Certification Needs: If you need a formal certification or notarization, there are extra administrative steps involved, which adds to the final bill.
While AI tools can give you a predictable and often lower-cost starting point, you absolutely must factor in the cost of a human expert to review any document that has legal weight.
What Is a Realistic Turnaround Time?
This can vary wildly. An AI tool can spit out a translation of a 10-page document in a few minutes, but a certified human translation of that same file could easily take several business days.
For a really complex, multi-page legal document that needs a specialized lawyer-linguist to handle it, a week or even longer is a realistic timeframe. The best thing you can do is communicate your deadline clearly from the very beginning. This ensures the provider can actually meet your needs without cutting corners on quality.
A common mistake I see is companies assuming a bilingual colleague can handle official translations. Even if they're perfectly fluent, they don't have the specialized legal training. More importantly, they can't provide the certified attestations that courts and government agencies demand.
Using your own staff for anything more than a basic internal review is a huge risk. This is precisely why you need translation services for legal documents; they provide a legally defensible attestation of accuracy that an employee simply can't. If you're looking into language solutions more broadly, it's worth exploring the full scope of professional translation services to understand what's out there.
Any reputable provider will have a clear policy for revisions. If you find an error, they should fix it quickly and at no extra charge. That said, the best practice is always to have your own internal legal expert give the final translated document one last look before it's submitted. This two-step verification is your best bet for ensuring total accuracy.
For fast, secure, and format-preserving translations, trust DocuGlot. Our AI-powered platform delivers accurate results in over 100 languages while keeping your document's original layout perfectly intact. Get your translation at https://docuglot.com.
Tags
Ready to translate your documents?
DocuGlot uses advanced AI to translate your documents while preserving formatting perfectly.
Start Translating